Plastic Product -Vacuum forming vs Injection Moulding

What is Vacuum Forming?
Vacuum forming also recognised as thermoforming is a manufacturing process whereby plastic sheets are preheated in automated vacuum forming equipment until soft and malleable. The preheated sheet then makes contact with a mould or form and a vacuum source is turned on that sucks the sheet to the mould. When cool, the sheet takes the shape of the mould. It is then trimmed with die cut.
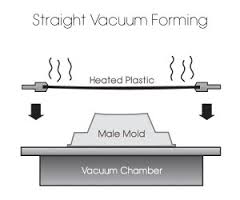
What is Injection Moulding?
The process of injection moulding begins with granules of polymer which are put in a hopper and released into a heated barrel. A screw feeds the material along the heated barrel where it is plasticised. The then liquid polymer is injected into a steel or aluminium mould through a gate, being held in a press under acute pressure. Post cooling, the mould opens and the finished parts are ejected from the mould.
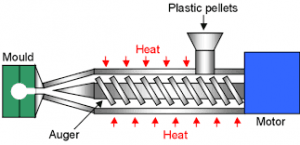
Process
| Process | Vacuum Forming | Injection Mould | |
| Tooling | A single 3D form created out of aluminium | A double-sided 3D mold is created out of steel, aluminium or a beryllium-copper alloy. | |
| Materials | Flat sheet of Thermoplastic available in a wide varienty of materials,finishes,colors and thicknesses | Thermoplastic pellets , available in a wide variety materials and colors. | |
| Production | A flat of plastic is heated to a pliable temperature,then molded to the tools shape using either suction from a vacuum or both suction and pressure | The plastic pellets are heated to a liquid state, then injected into the mold. | |
| Finishing | The final pieces are trimmed robotically, then can be used uncoated or painted, silk screened or have specialty coatings applied. | The final pieces are moved from the mold, then often need to be painted for aesthetic reasons and can also be silk screeened or have specialty coatings. |
Advantages Vacuum Forming & Injection Moulding
| Advantages Vacuum Forming | Advantanges Injection Moulding | |
| 1) Reasonably fast prototyping and production time frames | 1) Inserts can be used within the mould, and fillers added for strength | |
| 2) Ability to create large parts (up to 48 inches x 70 inches) | 2) Close tolerances on small intricate parts are achievable | |
| 3) Lower start-up costs — patterns and moulds can be made economically from MDF, high density foams and epoxy | 3) Ejected parts normally have a very finished look | |
| 4) Ideal for repeat jobs — aluminium castings can be made which have practically unlimited lifetimes | 4) Low levels of waste – scrap can be reground to be reused | |
| 5) Good price point on small and medium runs | 5) Allows for high production runs |
Disadvantages Vacuum Forming & Injection Moulding
| Disadvantages Vacuum Forming | Disadvantanges Injection Moulding | |
| 1) Consistent wall thickness is not achievable, very deep parts can be challenging | 1) Higher start-up costs | |
| 2) Only one material can be formed at a time | 2) Requires an intense level of engineering expertise and time | |
| 3) Higher per-piece costs make vacuum forming non-competitive with other computerised processes where quantities are higher | 3)Longer time frames due to manufacture of mould | |
| 4) Some clear parts will exhibit mark-off (defects or dirt from mould will transfer to parts) |
To conclude, both processes have their strengths and weaknesses. In determining which method is best for your particular product would recommend that you consider the following issues:
- Production quantity
- Design & Engineering requirements
- Time frame
- Start-up costs & Budget



